Table of Contents
Blocking TCP sockets in Java
Blocking Socket server source code
package org.ait;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
ServerSocket providerSocket;
Socket connection = null;
ObjectOutputStream out;
ObjectInputStream in;
String message;
Server() {
}
void run() {
try {
// 1. create a socket server listening to port 8080
providerSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
// 2. waiting for the connection (here we are waiting until next connection)
connection = providerSocket.accept();
// 3. create Input and Output streams
out = new ObjectOutputStream(connection.getOutputStream());
in = new ObjectInputStream(connection.getInputStream());
// 4. socket communication
do {
try {
message = (String) in.readObject();
System.out.println("client>" + message);
if (message.equals("bye")) {
sendMessage("bye");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException classnot) {
System.err.println("Data received in unknown format");
}
} while (!message.equals("bye"));
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4: close connection
try {
in.close();
out.close();
providerSocket.close();
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
void sendMessage(String msg) {
try {
out.writeObject(msg);
out.flush();
System.out.println("server>" + msg);
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Server server = new Server();
while (true) {
server.run();
}
}
}
Blocking Socket client source
package org.ait;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class Client {
Socket requestSocket;
ObjectOutputStream out;
ObjectInputStream in;
String message;
Client() {
}
void run() {
try {
// 1. try to connect to the socket: localhost:8080
requestSocket = new Socket("localhost", 8080);
// 2. Input and Output streams
out = new ObjectOutputStream(requestSocket.getOutputStream());
in = new ObjectInputStream(requestSocket.getInputStream());
// 3: communications
do {
try {
sendMessage("Hello server");
sendMessage("bye");
message = (String) in.readObject();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("data received in unknown format");
}
} while (!message.equals("bye"));
} catch (UnknownHostException unknownHost) {
System.err.println("You are trying to connect to an unknown host!");
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4: close connection
try {
in.close();
out.close();
requestSocket.close();
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
void sendMessage(String msg) {
try {
out.writeObject(msg);
out.flush();
System.out.println("client>" + msg);
} catch (IOException ioException) {
ioException.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Client client = new Client();
client.run();
}
}
Blocking UDP sockets in Java
The following Agent sends a message and waits for a response on port 8080, also with UDP. Older versions of the Eclipse IDE, the text you type on the console can be sent by pressing ctrl+z
package org.ait;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
public class UDPClient {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
BufferedReader inFromUser = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
DatagramSocket clientSocket = new DatagramSocket();
InetAddress IPAddress = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
byte[] sendData = new byte[1024];
byte[] receiveData = new byte[1024];
String sentence = inFromUser.readLine();
sendData = sentence.getBytes();
DatagramPacket sendPacket = new DatagramPacket(sendData, sendData.length, IPAddress, 8080);
clientSocket.send(sendPacket);
DatagramPacket receivePacket = new DatagramPacket(receiveData, receiveData.length);
clientSocket.receive(receivePacket);
String modifiedSentence = new String(receivePacket.getData());
System.out.println("converted:" + modifiedSentence);
clientSocket.close();
}
}
The UDP server waits for the agents messages on port 8080 and converts them to uppercase letters and sends them back to the client UDP socket.
package org.ait;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
public class UDPServer {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket serverSocket = new DatagramSocket(8080);
byte[] bytesReceived = new byte[1024];
byte[] bytesSent = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket receivePacket = new DatagramPacket(bytesReceived, bytesReceived.length);
// here we are waiting for the packets
serverSocket.receive(receivePacket);
String textMessage = new String(receivePacket.getData());
System.out.println("I got: " + textMessage);
InetAddress IPAddress = receivePacket.getAddress();
int port = receivePacket.getPort();
String upperCaseText = textMessage.toUpperCase();
bytesSent = upperCaseText.getBytes();
// send back
DatagramPacket sendPacket = new DatagramPacket(bytesSent, bytesSent.length, IPAddress, port);
serverSocket.send(sendPacket);
serverSocket.close();
}
}
Non-blocking TCP sockets in Java
Reading:
Non-blocking loop
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); // ez a sor jelzi a blokkolásmentes működést
while(true){
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if(socketChannel != null){
// the connection is accepted
}
}
Non-blocking Java client example
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Random;
public class Client implements Runnable {
private String host;
private int port;
// Bounds on how much we write per cycle
private static final int minWriteSize = 1024;
private static final int maxWriteSize = 65536;
// Bounds on how long we wait between cycles
private static final int minPause = (int) (0.05 * 1000);
private static final int maxPause = (int) (0.5 * 1000);
// Random number generator
Random rand = new Random();
public Client(String host, int port, int numThreads) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; ++i) {
new Thread(this).start();
}
}
public void run() {
byte buffer[] = new byte[maxWriteSize];
try {
Socket s = new Socket(host, port);
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
while (true) {
int numToWrite = minWriteSize
+ (int) (rand.nextDouble() * (maxWriteSize - minWriteSize));
for (int i = 0; i < numToWrite; ++i) {
buffer[i] = (byte) rand.nextInt(256);
}
out.write(buffer, 0, numToWrite);
int sofar = 0;
while (sofar < numToWrite) {
sofar += in.read(buffer, sofar, numToWrite - sofar);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " wrote " + numToWrite);
int pause = minPause + (int) (rand.nextDouble() * (maxPause - minPause));
try {
Thread.sleep(pause);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
}
} catch (IOException ie) {
ie.printStackTrace();
}
}
static public void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
new Client("localhost", 4444, 3);
}
}
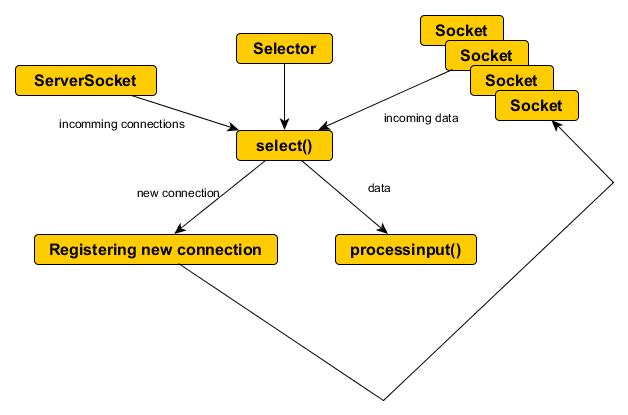
Non-blocking Java server example
public class Server implements Runnable {
// The port we will listen on
private int port;
// A pre-allocated buffer for encrypting data
private final ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16384);
public Server(int port) {
this.port = port;
new Thread(this).start();
}
public void run() {
try {
// Instead of creating a ServerSocket,
// create a ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// Set it to non-blocking, so we can use select
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
// Get the Socket connected to this channel, and bind it
// to the listening port
ServerSocket ss = ssc.socket();
InetSocketAddress isa = new InetSocketAddress(port);
ss.bind(isa);
// Create a new Selector for selecting
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// Register the ServerSocketChannel, so we can
// listen for incoming connections
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("Listening on port " + port);
while (true) {
// See if we've had any activity -- either
// an incoming connection, or incoming data on an
// existing connection
int num = selector.select();
// If we don't have any activity, loop around and wait
// again
if (num == 0) {
continue;
}
// Get the keys corresponding to the activity
// that has been detected, and process them
// one by one
Set keys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator it = keys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
// Get a key representing one of bits of I/O
// activity
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) it.next();
// What kind of activity is it?
if ((key.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) == SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) {
System.out.println("acc");
// It's an incoming connection.
// Register this socket with the Selector
// so we can listen for input on it
Socket s = ss.accept();
System.out.println("Got connection from " + s);
// Make sure to make it non-blocking, so we can
// use a selector on it.
SocketChannel sc = s.getChannel();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
// Register it with the selector, for reading
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if ((key.readyOps() & SelectionKey.OP_READ) == SelectionKey.OP_READ) {
SocketChannel sc = null;
try {
// It's incoming data on a connection, so
// process it
sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
boolean ok = processInput(sc);
// If the connection is dead, then remove it
// from the selector and close it
if (!ok) {
key.cancel();
Socket s = null;
try {
s = sc.socket();
s.close();
} catch (IOException ie) {
System.err.println("Error closing socket "
+ s + ": " + ie);
}
}
} catch (IOException ie) {
// On exception, remove this channel from the
// selector
key.cancel();
try {
sc.close();
} catch (IOException ie2) {
System.out.println(ie2);
}
System.out.println("Closed " + sc);
}
}
}
// We remove the selected keys, because we've dealt
// with them.
keys.clear();
}
} catch (IOException ie) {
System.err.println(ie);
}
}
// Do some cheesy encryption on the incoming data,
// and send it back out
private boolean processInput(SocketChannel sc) throws IOException {
buffer.clear();
sc.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
// If no data, close the connection
if (buffer.limit() == 0) {
return false;
}
// Simple rot-13 encryption
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.limit(); ++i) {
byte b = buffer.get(i);
if ((b >= 'a' && b <= 'm') || (b >= 'A' && b <= 'M')) {
b += 13;
} else if ((b >= 'n' && b <= 'z') || (b >= 'N' && b <= 'Z')) {
b -= 13;
}
buffer.put(i, b);
}
sc.write(buffer);
System.out.println("Processed " + buffer.limit() + " from " + sc);
return true;
}
static public void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
new Server(4444);
}
}