This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
1. What is CSS?
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a fundamental technology used in web development to control the formatting and layout of HTML documents. While HTML provides the structure and content of a web page, CSS allows developers to apply styles, such as colors, fonts, spacing, and positioning, to create visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces.
2. Selectors and declarations
CSS is built around selectors and declarations.
Selectors specify which HTML elements the styles should target. They can be as simple as selecting an element by its name (e.g., p for all paragraph elements) or as targeting elements based on classes, IDs, attributes.
Declarations define the style properties and their values that should be applied to the selected elements. A declaration consists of a property (e.g., color) and a value (e.g., blue), separated by a colon and enclosed in curly braces. For example, p { color: blue; } changes the text color of all paragraphs to blue.
Let's see it in a very simple example:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Blue Paragraph</title> <style> p { color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <p>This is a blue paragraph.</p> <p>This is also a blue paragraph.</p> </body> </html>
3. Defining CSS styles
Inline
Inline styles are specified in the style attribute of an HTML element.
<p style="color: red; font-size: 16px;">This is red paragraph with 16px sized text.</p>
Embedded
Styles can also be embedded within the HTML page using the <style> element in <head>.
<head> <style> h1 { color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Blue Heading</h1> </body>
External File
Styles can be imported from an external file using the <link> element.
<head> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> </head>
4. CSS comments
CSS comments are placed between /.
/* This is a CSS comment,
which can span multiple lines. */
5. Element, ID, and class Selectors
* Element selector: Applies to all specified elements. * ID selector: Targets a specific element based on its unique ID. * Class selector: Targets one or more elements with a specific class.
/* Element selector, applies to all paragraphs */ p { color: blue; } /* ID selector, applies to the element with the specific ID "header" */ #header { font-size: 24px; } /* Class selector, applies to all elements with the class "button" */ .button { background-color: green; }
6. Cascading
When multiple rules target the same selector, the later rule will override the previous one.
<head> <style> p { color: red; } p { color: green; } </style> </head> <body> <p>This paragraph will be green.</p> </body>
7. Role of ''span'' and ''div'' elements
* span: An inline element, which is used to mark a portion of text.
* div: A block element, which is used to group multiple contents into a block.
<p>This is a <span style="color: red">red</span> text.</p> <div style="font-weight: bold"> <p>This is bold text.</p> <p>So is this.</p> <p>And this too.</p> </div>
8. Background styling
The background property defines the background style of an element.
body { background-color: #f0f0f0; } #header { background-image: url('header.jpg'); }
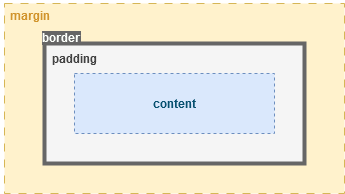
9. Margin, padding and border
The margin is the outer space around an element, while the padding is the inner space between the content and the border. The border defines the outline of the element. This is called the “box model.”
div { margin: 10px; padding: 20px; border: 1px solid black; border-radius: 5px; }
10. Setting width and height
The width and height properties allow you to set the dimensions of an element.
img { width: 100px; height: 100px; }
11. Text styling
There are several properties available for text formatting.
p { font-family: Arial; font-size: 16px; font-weight: bold; font-style: italic; text-decoration: underline; text-align: justify; }
12. Exercise
Create the following webpage by using HTML and CSS. Use inline CSS for formatting the text, and also apply class-based and id-based selectors!
Feel free to use online resources (e.g. W3Schools CSS tutorial) as help.
Raw text:
John von Neumann “Young man, in mathematics you don't understand things. You just get used to them.” John von Neumann John von Neumann (born János Lajos Neumann) (Budapest, December 28, 1903 - Washington, February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-born mathematician. In addition to his theoretical research in quantum mechanics, he became famous for laying the foundations of the digital computer. John von Neumann Image: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/JohnvonNeumann-LosAlamos.jpg/462px-JohnvonNeumann-LosAlamos.jpg Born: December 28, 1903 Died: February 8, 1957 (aged 53) Known for: Mathematician, computer scientist, physicist, professor Citizenship: Hungarian, American Education: - Budapest-Fasori Evangelical Gymnasium - Friedrich Wilhelm University - Royal Hungarian Pázmány Péter University - Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich - University of Göttingen Neumann made tremendous contributions to mathematics, quantum mechanics, quantum theory, game theory, economics, and computer science. Several concepts and principles are associated with his name, such as the Neumann principle in quantum mechanics, the Neumann stability theory in game theory, and the Neumann process in numerical analysis. John von Neumann was one of the most significant figures in computer science. He was among the first to recognize the potential of digital computers. Neumann developed fundamental concepts and architectures that have become foundational in the design and operation of modern computers. He is known for the "von Neumann architecture", which is a computer architecture where programs and data are stored in the same memory. John von Neumann was an incredibly versatile scientist, and his research had a profound impact on computer science, mathematics, and other scientific fields. His work and legacy continue to influence modern scientific and technological developments.